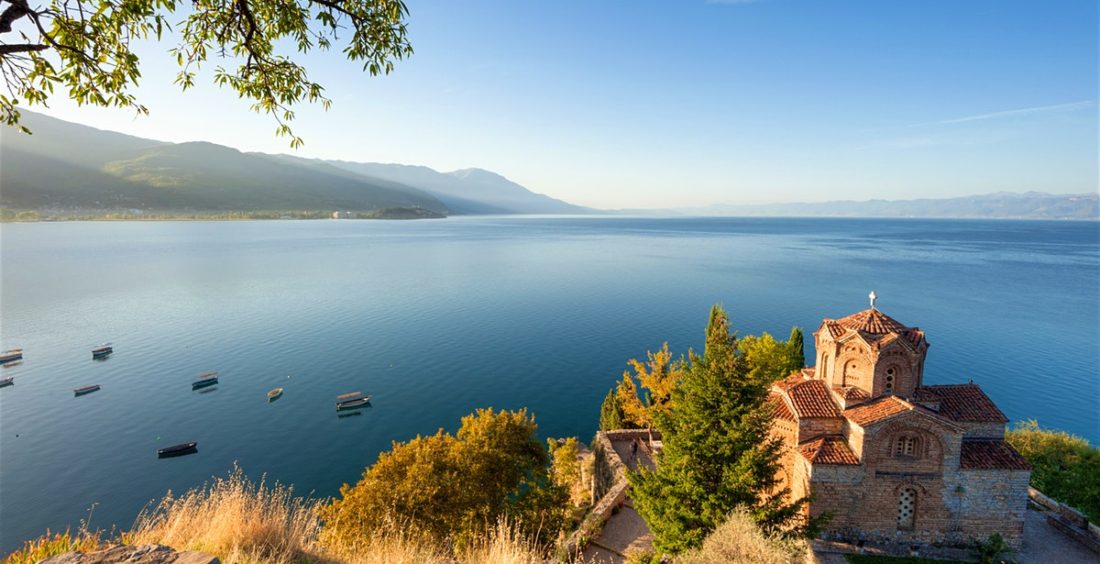
The Lake Ohrid region, a mixed World Heritage property covering c. 94,729 ha, was first inscribed for its nature conservation values in 1979 and for its cultural heritage values a year later. These inscriptions related to the part of the lake located in North Macedonia. The property was extended to include the rest of Lake Ohrid, located in Albania, in 2019.
Lake Ohrid is a superlative natural phenomenon, providing refuge for numerous endemic and relict freshwater species of flora and fauna dating from the tertiary period. As a deep and ancient lake of tectonic origin, Lake Ohrid has existed continuously for approximately two to three million years. Its oligotrophic waters conserve over 200 species of plants and animals unique to the lake, including algae, turbellarian flatworms, snails, crustaceans and 17 endemic species of fish including two species of trout, as well as a rich birdlife.
The town of Ohrid is one of the oldest human settlements in Europe. As one of the best preserved complete ensembles encompassing archaeological remains from the Bronze Age up to the Middle Ages, Ohrid boasts exemplary religious architecture dating from the 7th to 19th centuries as well as an urban structure showcasing vernacular architecture from the 18th and 19th centuries. All of them possess real historic, architectural, cultural and artistic values. The concentration of the archaeological remains and urban structures within the old urban centre of Ohrid, in the Lin Peninsula, and along the coast of Lake Ohrid as well as the surrounding areas creates an exceptional harmonious ensemble, which is one of the key features that make this region truly unique.
The property encompasses all of the features that convey the property’s Outstanding Universal Value in relation to natural and cultural criteria.



 Rruga e Elbasanit, Pallati nr. 111,
Rruga e Elbasanit, Pallati nr. 111,